Overview
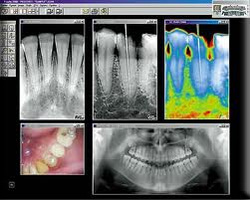
Traditional film radiography has served the profession ably for over a century. Since the unveiling of filmless digital radiographic prototypes in the early eighties, many new efficiencies have been introduced to this diagnostic staple. Two basic formats (electronic sensor and phosphor plate) exist and all standard types of intra and extra oral imaging are possible with them, Both have the not to be underestimated advantage of reduced radiation exposure to the patient. This has been a practice builder for me whereby patients perceive my office as both having cutting edge technology and being sensitive to their health concerns. A relatively newer radiographic modality, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT - e.g., I-cat), could not exist without the benefits of digital technology and this process has become essential to better implant dentistry and endodontics.
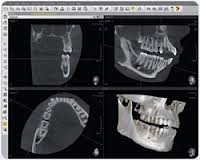
From a practical standpoint, both formats eliminate the need for and associated costs of film, processing chemicals and their disposal from your dental office. This presents a significant long term savings that will allow this technology to pay for itself in a relatively short period of time. The larger views and software manipulation available with digital systems enhance diagnostic capabilities while improving patient education. The electronic format allows more effective image sharing capacity between health care providers and even to third party payers. The speed of some systems greatly facilitates endodontic treatment while the similarity to conventional film of others both increases patient comfort considerably while reducing the learning curve for your staff.
Learning Objectives
After this course, the attendee should be able to:
- Identify the two basic formats of digital radiography systems and the pros and cons of each.
- Understand the cost savings associated with digital radiography and its effect on your bottom line.
- Describe the software programs used to manipulate digital radiographs and detail their parameters.
- Discuss the importance of reduced radiation exposure levels to patients using digital radiography.
- Explain the increased image sharing potential available to all parties involved with patient care.
